- Collateralized debt obligations (CDOs) are bundles of debt that banks package deal for resale to buyers.
- CDOs are troublesome to guage, as a result of the entire money owed are lumped collectively.
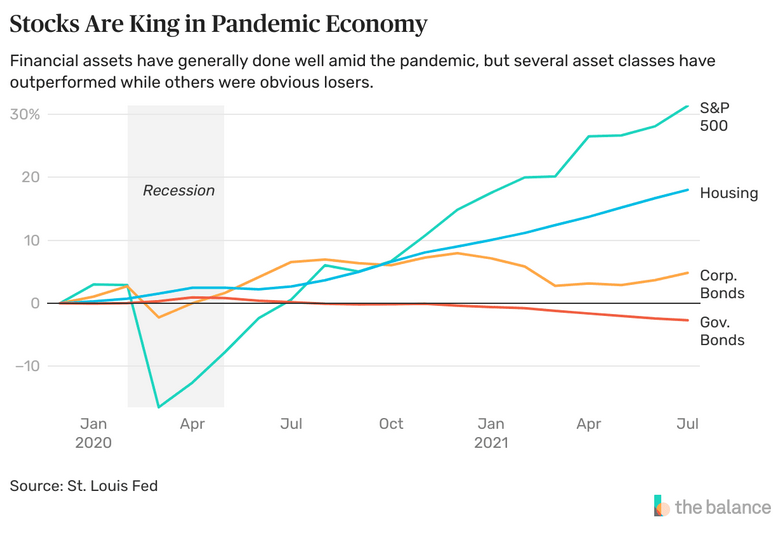
- CDOs at first drove the financial system earlier than they escalated past management and led to the crash of 2007.
- CDOs had fallen out of favor as an funding car, however by 2012 that they had already began coming again underneath considerably completely different buildings.
What Are Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs)?
CDOs, or collateralized debt obligations, are monetary instruments banks use to repackage particular person loans into merchandise offered to buyers on the secondary market. These packages include auto loans, bank card debt, mortgages, or company debt. They’re known as “collateralized” as a result of the promised repayments of the loans are the collateral that provides the CDOs their worth.
Collateralized debt obligations are a specific type of by-product. Derivatives are merchandise that derives their worth from one other underlying asset. Like put choices, name choices, and futures contracts, derivatives have lengthy been used within the inventory and commodities markets.
- Alternate identify: Collateralized mortgage obligations (CLOs) are CDOs made up of financial institution debt.
- Acronym: CDO
How CDOs Work
CDOs are known as “asset-backed industrial paper” in the event that they include company debt. Banks name them “mortgage-backed securities” if the loans are mortgages. If the mortgages are made to these with a less-than-prime credit score historical past, they’re known as “subprime mortgages.”
Banks promote CDOs to buyers for 3 causes:
- The funds they obtain give them additional cash to make new loans.
- The method strikes the loans’ threat of default from the financial institution to the buyers.
- CDOs give banks new and extra worthwhile merchandise to promote, which boosts share costs and managers’ bonuses.
Word
At first, CDOs have been a welcome monetary innovation. They supplied extra liquidity within the financial system. CDOs allowed banks and firms to dump their debt, thereby releasing up extra capital to take a position or lend.
Notable Happenings
At first, the unfold of CDOs was a great addition to the U.S. financial system. The invention of CDOs additionally helped to create new jobs.
Not like a mortgage on a home, a CDO is just not a product you’ll be able to contact or see to search out out its worth. As an alternative, a pc mannequin creates it. After the invention of CDOs, 1000’s of faculty and higher-level graduates went to work in Wall Avenue banks as “quant jocks.” Their job was to jot down laptop applications that will mannequin the worth of the bundle of loans that made up CDOs. Hundreds of salespeople have been additionally employed to search out buyers for these new merchandise.
The Rise of CDOs
Though CDOs fell out of favor after the monetary disaster of 2007, they started to creep again into the market in 2012.
Adjustable-rate mortgages provided “teaser” low-interest charges for the primary three to 5 years. Larger charges kicked in after that. Debtors took the loans, realizing they might solely afford to pay the low charges. They anticipated to promote their homes earlier than the upper charges have been triggered.
The quant jocks designed CDO tranches to reap the benefits of these completely different charges. One tranche held solely the low-interest portion of mortgages. One other tranche provided simply the half with the upper charges. That approach, conservative buyers may take the low-risk, low-interest tranche, whereas aggressive buyers may take the higher-risk, higher-interest tranche. All went properly so long as housing costs and the financial system continued to develop.
What Went Flawed With CDOs
Sadly, the additional liquidity created an asset bubble in housing, bank cards, and auto debt. Housing costs skyrocketed past their precise worth. Individuals purchased houses simply so they might promote them. The straightforward availability of debt meant that individuals used their bank cards an excessive amount of. That drove bank card debt to nearly $1 trillion in 2008.
The banks that offered the CDOs did not fear about individuals defaulting on their debt. They’d offered the loans to different buyers, who then owned them. That made them much less disciplined in adhering to strict lending requirements. Banks made loans to debtors who weren’t creditworthy, which ensured catastrophe.
Word
From the patrons’ perspective, CDOs could have grow to be too difficult. The patrons did not know the worth of what they have been shopping for. They relied on their belief within the banks promoting the CDOs.
Patrons could not have performed sufficient analysis to make sure the CDO packages have been value their costs, however analysis would not have performed a lot good, as a result of even the banks did not know. The pc fashions primarily based the CDOs’ worth on the belief that housing costs would proceed to go up. In the event that they have been to fall, the computer systems could not value the merchandise.
This opacity and the complexity of CDOs created a market panic in 2007. Banks realized that they could not value the merchandise or the property they have been nonetheless holding. In a single day, the marketplace for CDOs disappeared. Banks refused to lend one another cash, as a result of they did not need extra CDOs on their stability sheets in return.
It was like a monetary sport of musical chairs when the music stopped, and ensuing panic brought about the 2007 banking disaster.
The Position of CDOs within the Subprime Mortgage Disaster
The primary CDOs to go decline have been the mortgage-backed securities. When housing costs began to drop in 2006, the mortgages on houses purchased in 2005 have been quickly “the other way up,” in flip creating the subprime mortgage disaster. The Federal Reserve assured buyers that the disaster was confined to housing. The truth is, some welcomed it and mentioned that housing costs had been in a bubble and wanted to chill down.
What they did not understand was how derivatives multiplied the impact of any bubble and any subsequent downturn. Not solely banks have been left holding the bag, however so have been pension funds, mutual funds, and firms. It wasn’t till the Federal Reserve and the Treasury began shopping for these CDOs {that a} semblance of functioning returned to the monetary markets.
The Dodd Frank-Wall Avenue Reform Act of 2010 was adopted with the intention of stopping the identical type of publicity that led to a number of banks’ collapse through the disaster. This federal legislation was weakened in 2017, when small banks have been faraway from protection, and the Trump administration sought to repeal it altogether.