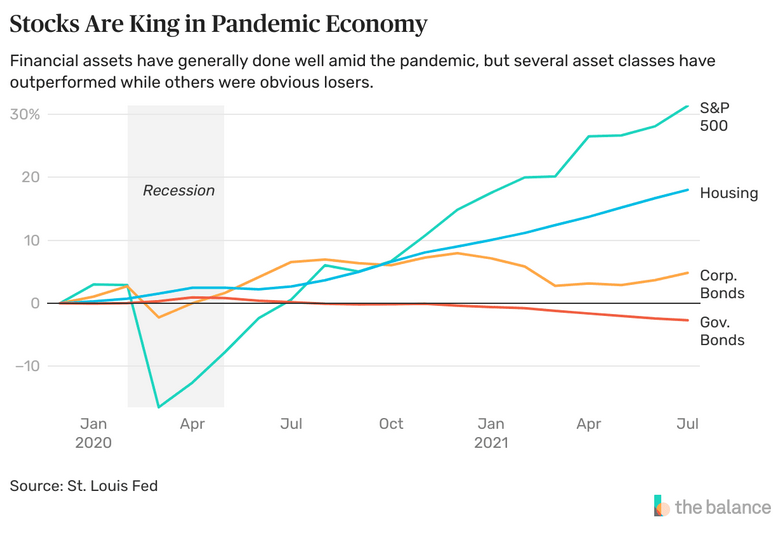
A reverse inventory cut up is a company transaction that consolidates shares and subsequently will increase the person share worth. An organization could need to improve its share worth to draw buyers or to stay in compliance with share worth requirements on its alternate.
Let’s evaluate how a reverse inventory cut up works, why firms could use them, and what buyers ought to learn about them.
Definition and Instance of a Reverse Inventory Break up
Reverse inventory splits are when firms consolidate shares, usually to extend the share worth. Every share is transformed right into a fractional share, and the share worth is elevated by the quantity of the reverse cut up.
For instance, say a inventory was priced at $1 per share and an investor owned 500 shares. After a 1:10 (one for 10) reverse cut up, the inventory would commerce for $10 per share, and the identical investor would personal 50 shares.
Be aware
Reverse inventory splits and inventory splits don’t replicate a change within the intrinsic worth of the corporate—solely the share worth, which adjusts. However the market cap of the corporate shouldn’t be instantly affected by a reverse cut up or cut up.
Firms usually reverse cut up their shares to both improve buying and selling quantity by attracting extra buyers with the next share worth, or to remain listed on a inventory alternate by remaining in compliance with the alternate’s share worth requirements. Exchanges such because the New York Inventory Alternate (NYSE) and Nasdaq have itemizing necessities that embrace share worth and quantity staying above sure ranges.
A latest instance is the 1:8 reverse cut up that Normal Electrical (GE) underwent in 2021. Shareholders authorized the reverse cut up in Might to align GE’s share worth and numbers of shares excellent with equally sized rivals after the corporate divested a number of subsidiaries.
Previous to the reverse cut up, which befell on August 2, 2021, the inventory traded within the low teenagers. On the day of the cut up, it traded for round $104 per share. Over the subsequent six months, it traded as little as $92 per share. This illustrates a danger buyers face with reverse inventory splits, which is that they will lose cash on account of the fluctuations in costs after the cut up.
Reverse inventory splits usually are introduced a number of weeks to months upfront.
How Does a Reverse Inventory Break up Work?
Reverse inventory splits will not be ruled by the U.S. Securities and Alternate Fee (SEC) like different company actions. Typically, the cut up have to be authorized by both the board of administrators or shareholders, relying on the corporate’s bylaws and state company regulation.
Be aware
Public firms that file with the SEC can notify shareholders about an upcoming reverse inventory cut up with a proxy assertion on kinds 8-Ok, 10-Q, or 10-Ok. They might be required to file a proxy assertion through Schedule 14A if shareholder approval is required. If the corporate goes non-public on account of a reverse inventory cut up, the corporate would wish to file a proxy assertion on Schedule 13E-3.
On the day of the cut up, each current share is transformed right into a fractional share. When Normal Electrical did its reverse cut up, every share turned one-eighth of a share. In different phrases, buyers acquired one share for each eight shares they owned. Nevertheless, the overall worth of their funding remained the identical.
Buyers who don’t personal quite a lot of shares which can be divisible by the reverse cut up ratio will both have fractional shares in consequence, or the corporate pays the investor money for these fractions. The exception to fractional shares is when an organization does a reverse cut up as a mechanism for going non-public. Companies can deregister from the SEC if they’ve fewer than 300 shareholders, and one approach to get under that quantity is with a reverse cut up that eliminates most marginal holders.
For instance, if most shareholders of a inventory personal fewer than 1,000 shares, the corporate can do a 1:1,000 reverse cut up and squeeze out the buyers who personal fewer shares by paying them for his or her holdings. These shareholders would both have to simply accept that worth or purchase extra shares to whole 1,000.
If the corporate units a worth for small shareholders that’s above the present market worth (to incentivize buyers to promote their inventory), there could also be an arbitrage alternative. Utilizing the instance above, buyers may purchase 999 shares on the present market worth and make a revenue when squeezed out by the reverse cut up.
Reverse Inventory Break up vs. Inventory Break up
A inventory cut up is the other of a reverse inventory cut up. On this case, an organization that has a excessive share worth will increase the variety of shares excellent to cut back the value of the inventory. That is usually achieved to maintain the inventory worth inexpensive for particular person buyers.
A latest instance is Intuitive (ISRG), which had a 3:1 cut up on Oct. 5, 2021. On this case, buyers acquired three shares for each one share they held.
Be aware
A inventory cut up is just like a reverse inventory cut up in that they’re each usually achieved to extend investor curiosity and quantity within the inventory. One is completed as a result of the inventory worth is simply too low and the opposite is completed as a result of it’s too excessive. In each instances, the investor maintains their holdings, however with a unique variety of shares.
What It Means for Particular person Buyers
Reverse inventory splits usually happen as a result of an organization desires to boost its inventory worth. Firms with shares which can be priced too low might be excluded from exchanges such because the NYSE or the Nasdaq.
Buyers’ holdings will not be instantly affected by a reverse inventory cut up, however ensuing fluctuations within the share worth that would observe could trigger buyers to lose cash.
Buyers ought to analysis their funding selections, together with an organization’s motivation behind a reverse inventory cut up.
- Reverse inventory splits are achieved to extend a inventory’s worth by decreasing the variety of shares.
- Firms conduct reverse inventory splits to draw extra curiosity from buyers, to keep away from delisting from a inventory alternate, or to go non-public.
- A 1:10 inventory cut up would scale back each current share to one-tenth of a share and improve the share worth tenfold.